Learning about fungi is hard enough even for infectious disease fellows (Narrator: especially for infectious disease fellows). By the time you learn how to differentiate the yeasts from the molds, the fungi kingdom decides to throw you a curve ball: Enter the shape shifters into the game of fungi learning – the dimorphic fungi.
The Dimorphic fungi shape shift depending on the weather (literally). They exist as molds in the great outdoors (environmental temperatures) and yeasts in the great indoors (inside our bodies at body temperatures). Clinically, this also means you will see the yeast forms in a histopathology review of a tissue sample, and our friends in the microbiology lab can re-create the environmental factors to grow them out as mold forms in culture. So essentially, they also shape shift between the microbiology lab and the pathology department. (They are sneaky Fung(uy)i…)
This is the first post out of 6 and will focus on our first shapeshifter, Histoplasma capsulatum.
CLICK HERE for a 2-page PDF handout of this information.
Morphology:(3)
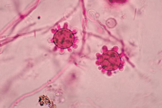
- At 25°C-30°C (mold form):Young cultures – septate hyphae with smooth or spiny microconidia
- Older cultures (several weeks old) – large, thick walled round macroconidia with knobby projections (Image)
- At 37°C (yeast form): small, round budding cells
Geography, Reservoir and Mode of Transmission:
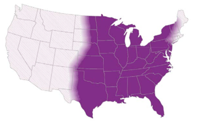
- Histoplasma has a world-wide distribution(4), but is mostly endemic in the Americas (Central/Eastern United States & Central and South America)
- Reservoir includes: soil, areas of construction, animal droppings (i.e. bats – a board favorite!), and caves (another board favorite)
- Mode of transmission: aerogenic
Clinical presentation:
- Known as the ‘syphilis’ of the fungal world because it’s a great imitator, particularly of TB(4).
- Disease presentation/severity depends on size of inoculum & immune status
- Immunocompetent hosts: usually asymptomatic/self- limiting
- Immunocompromised hosts: often progressive/severe/disseminated
- Can present as:
- Acute pulmonary disease: Either as diffuse or localized infiltrates +/- mediastinal lymphadenopathy
- Chronic pulmonary disease: Cavitary lesions/nodules
- Mediastinal disease: Mediastinal granulomas and fibrosis
- Disseminated disease to extra pulmonary sites such as: spleen, adrenal glands, oral mucosa (ulcers), bone marrow, etc
Diagnosis:
1. Culture:
- *Please alert the microbiology lab if you suspect histoplasmosis and are sending them cultures! (culture needs to be specially handled in the lab due to risk occupational transmission/infection (just like all dimorphic fungi covered in this review).
- Sensitivity of both tissue and blood cultures depend on the presentation (pulmonary vs. disseminated), immune status and burden of disease(5)
- Disseminated disease → ~74% will have positive cultures(6)
- Pulmonary disease → ~42% will have positive cultures(6)
- HIV/AIDS patients:
→ ~ 90% of respiratory cultures will be positive(7)
→~50% of blood cultures will be positive(7)
2. Histopathology:
- Appear as yeast form, predominantly phagocytosed within macrophages and histiocytes
- Presence in tissue supports diagnosis, although does not necessarily indicate active infection (could be detected in non-active granulomas for years)
- Characteristic pathology feature is the presence of granulomas (caseating or non-caseating)(6)
3. Antigen detection:
- Preferred method of testing: rapid testing + non-invasive + highly sensitive.
- Sensitivity: urinary antigen > serum antigen (across all spectrum of clinical presentations of histoplasmosis)(9)
- Histoplasma serum antigen (MiraVista© EIA) have highest sensitivity in disseminated disease (91.8%) >chronic pulmonary disease (87.5%) >acute pulmonary disease (83%) >subacute histoplasmosis (30%)(8)
- In HIV/AIDS patients with disseminated disease, Histoplasma antigen can be detected in 95% of cases
- Mediastinal involvement in histoplasmosis (mediastinal granuloma, mediastinitis) doesn’t usually result in positive antigen testing
- Histoplasma antigen can cross react with all the dimorphic fungi covered in this review series (less commonly for coccidioides spp.)
4. Serology:
- Antibodies take 4-8 weeks to become detectable therefore not useful for acute diagnosis but can be helpful for subacute and chronic forms of the disease
- Titers usually decrease with disease resolution, but slowly so titers cannot be used to monitor for treatment response
- Immunocompromised patients, particularly those with humoral defects, might not mount an antibody response so serology testing isn’t as useful.
5. Molecular methods:
- No currently FDA approved molecular assay for H. capsulatum for clinical use.
- PCR assays available in reference labs but are not yet standardized
Management(12):
| Clinical presentation | Mild/Moderate | Moderate/Severe | Chronic |
| Pulmonary | <4weeks: none >4weeks: itraconazole for 6-12 months | Lipid amphotericin B for 1-2 weeks followed by itraconazole for 12 weeks | Itraconazole for 12 months |
| Disseminated | Itraconazole for 12 months | Lipid amphotericin B for 1-2 weeks followed by itraconazole for 12 months | N/A |
References:
1. Climate change: the role of the infectious disease community. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017; 17:1219.
2. Greer A, Ng V, and Fisman D. Climate change and infectious diseases in North America: the road ahead. CMAJ. 2008; 178:715–722.
3. Walsh, TJ, Hayden, RT, and Larone, DH. Larone’s medically important fungi, 6th edition, ASM press, 2018.
4. Queiroz-Telles F, Fahal AH, Falci DR, et al. Neglected endemic mycoses. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:e367–e377.
5. Azar MM and Hage CA. Laboratory Diagnostics for Histoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2017; 55:1612–1620.
6. Hage CA, Azar MM, Bahr N, Loyd J, and Wheat LJ. Histoplasmosis: up-to-date evidence-based approach to diagnosis and management. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 36:729–745.
7. Kauffman CA. Histoplasmosis: a clinical and laboratory update. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007;20:115–132.
8. Hage CA, Ribes JA, Wengenack NL, et al. A multicenter evaluation of tests for diagnosis of histoplasmosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:448–454.
9. Wheat LJ and Kauffman CA. Histoplasmosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2003;17:1–19.
10. Swartzentruber S, Rhodes L, Kurkjian K, et al. Diagnosis of acute pulmonary histoplasmosis by antigen detection. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 49:1878–1882.
11. Saccente M and Woods GL. Clinical and laboratory update on blastomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23:367–381.
12. Wheat LJ, Freifeld AG, Kleiman MB, et al; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with histoplasmosis: 2007 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:807–825.
2 thoughts on “Histoplasma Capsulatum”