Learning about fungi is hard enough even for infectious disease fellows (Narrator: especially for infectious disease fellows). By the time you learn how to differentiate the yeasts from the molds, the fungi kingdom decides to throw you a curve ball: Enter the shape shifters into the game of fungi learning – the dimorphic fungi.
The Dimorphic fungi shape shift depending on the weather (literally). They exist as molds in the great outdoors (environmental temperatures) and yeasts in the great indoors (inside our bodies at body temperatures). Clinically, this also means you will see the yeast forms in a histopathology review of a tissue sample, and our friends in the microbiology lab can re-create the environmental factors to grow them out as mold forms in culture. So essentially, they also shape shift between the microbiology lab and the pathology department. (They are sneaky Fung(uy)i…).
If you haven’t read the first post on Histoplasma capsulatum, go read it now!
This is the 2nd post out of 6 and will focus on our second shapeshifter, Blastomyces dermatiditis.
CLICK HERE for a 2-page PDF handout of this information.
Morphology(1):
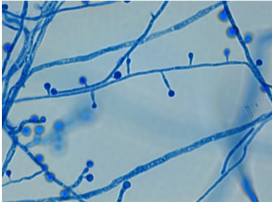
At 25°C-30°C (mold form): septate hyphae with short or long conidiophores where a pear-shaped conidia form at the apex of the conidiophore (has a lollipop-like appearance).
(Image A)
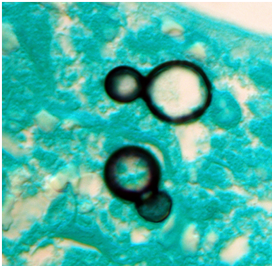
At 37°C (yeast form):
appear as yeast-like cells, thick walled and budding with a broad base
(Image B)
Geography, Reservoir and Mode of Transmission:
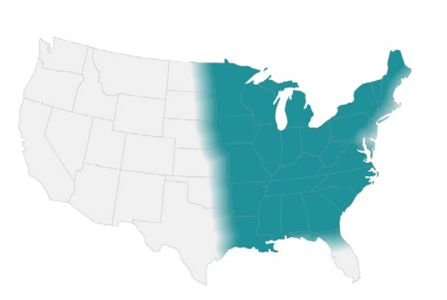
- Endemic in North America (Ohio & Mississippi river valleys and the Great Lakes region)
- Sporadic cases in Africa and India(2)
- Reservoir includes: moist soil with decaying vegetative matter, decomposed wood
- Mode of transmission: aerogenic, skin inoculation
Clinical presentation:
- Incubation period: 30-45 days (3)
- Spectrum of clinical disease:
- Asymptomatic disease – occurs in ~50% of individuals
- Acute pulmonary blastomycosis – resembles community-acquired pneumonia with variable presentation (infiltrates, consolidation +/- cavitation, reticulonodular patterns, small pleural effusions)(4)
- Chronic pulmonary blastomycosis – can mimic presentation of TB, lung cancer, and histoplasmosis. Radiographic pattern often is described as alveolar or fibronodular infiltrations, mainly with an upper lobe distribution. Absence of mediastinal lymph node involvement in blastomycosis can distinguish it from Histoplasmosis.(4)
- Extrapulmonary disease have been described in two-thirds of patients with chronic blastomycosis(3). Most frequent sites: skin, bones and genitourinary system.
- Patients frequently present with cutaneous lesions without clinically active pulmonary disease.
- CNS involvement is rare, except in immunocompromised hosts. As many as 40% of AIDs patients who have blastomycosis have CNS disease (mass lesions or meningitis)(5).
Diagnosis:
Your friendly Infectious disease doctors will alwaysask for tissue, and if classic broad-based budding yeast are appreciated in histopathology, that’s a slam dunk diagnosis! But we understand that is not always feasible, so in addition to clinical history + presentation, in order of importance:
- Tissue (histopathology, faster visualization, culture will have a long incubation time)
- Urine Antigen detection (keeping in mind issues with cross-reactivity as outlined below)
Culture:
*Please alert the microbiology lab if you suspect Blastomycosis and are sending them cultures! (culture needs to be specially handled in the lab due to risk occupational transmission/infection (just like all dimorphic fungi covered in this review series).
- Most sensitive method, however long incubation time
- For cutaneous lesions, important to obtain specimen from active leading edge
Histopathology:
- Forms non-caseating granulomas
- Classic appearance in clinical samples: Broad-based budding yeast (Image B, morphology)
Antigen detection:
High sensitivity for urine detection (93%) in largest published evaluation(2) but low specificity (79%) due to cross reactivity with Histoplasmosis, Paracoccidioidomycosis and Talaromycosis (previously known as penicilliosis)
Serology:
- No role in diagnosis because of poor sensitivity and high cross-reactivity(4)
Molecular methods:
- No commercially available tests
Management(3):
Pulmonary disease
- Mild to moderate: Itraconazole 6-12 months
- Moderate to severe: Lipid Amphotericin B for 1-2 weeks followed by → Itraconazole for 6-12 months
Disseminated disease
- Mild to moderate: Itraconazole for 6-12 months
- Moderate to severe: Lipid Amphotericin B for 1-2 weeks followed by → Itraconazole for 12 months
References:
1. Walsh TJ, Hayden RT, Larone DH. Larone’s medically important fungi, 6th edition, ASM press, 2018.
2. Saccente M and Woods GL. Clinical and laboratory update on blastomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23:367–381.
3. Chapman SW, Dismukes WE, Proia LA, Bradsher RW, Pappas PG, Threlkeld MG, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of blastomycosis: 2008 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008 Jun 15;46(12):1801-12
4. Salzer HJF, Burchard G, Cornely OA, et al. Diagnosis and management of systemic endemic mycoses causing pulmonary disease. Respiration; 2018;96:283–301.
5. Pappas PG, Pottage JC, Powderly WG, et al. Blastomycosis in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med;1992:116
1 thought on “Blastomyces species”